June 12, 2023
Economic Losses Due to Hay fever, a Japanese "National Disease," may Exceed 380 Billion Yen
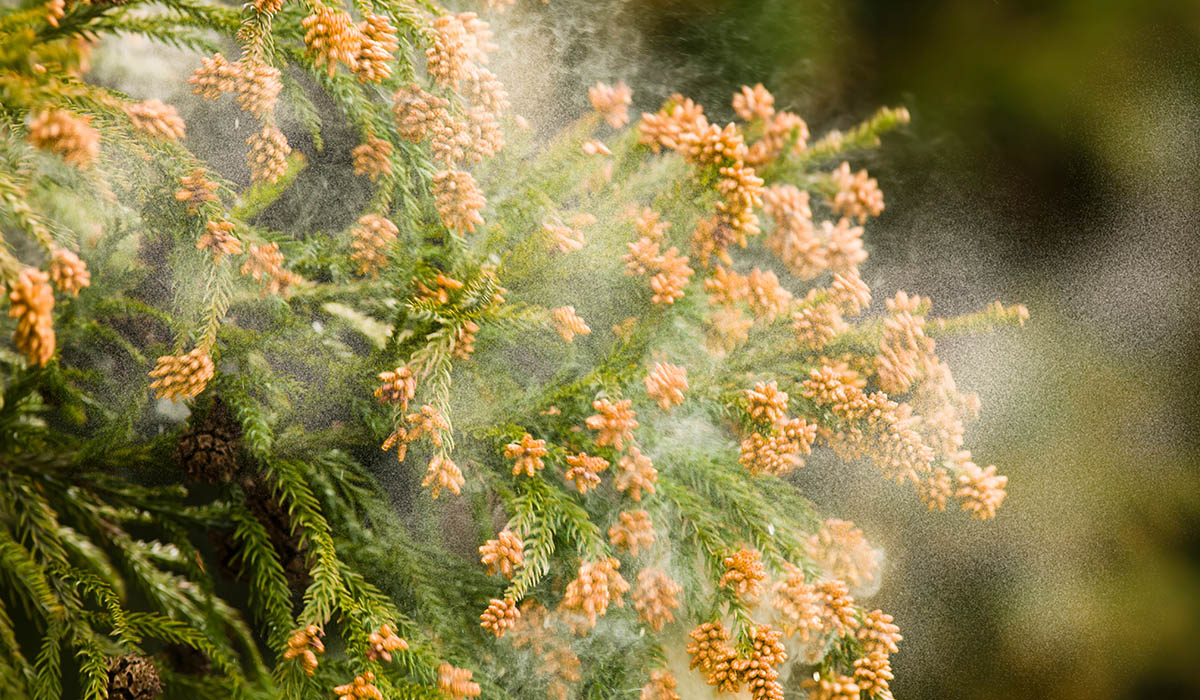
These figures became clear by private estimates. The government launched measures to curb health hazards and economic losses in May. The main focus will be to promote the cutting down and replanting of cedar trees that are the source of pollen. Efforts by the public and private sectors to develop applications for domestically produced cedar lumber are urgently needed.
Dai-ichi Life Research Institute released the person's estimate that 383.1 billion yen may have pushed down household consumption from January to March 2023 due to the massive dispersion of pollen. The decrease in outings by hay fever sufferers seems to have led to a drop in consumption, especially in the food service and leisure sectors.
Over this year's spring, we have had high pollen counts on many sunny days. In May, the government outlined measures such as halving pollen production in 30 years. Efforts will focus on promoting the harvesting and utilization of cedar trees that are the source of the problem.
With international forest conservation efforts and the expansion of planted forests in Japan, Japan's self-sufficiency rate for lumber has increased from a low of 18% in 2002 to 41% in 2021. It is essential to create stable demand to encourage the use of cedar lumber and further increase self-sufficiency.
Creating a virtuous cycle in which the public and private sectors work together to raise the demand for domestically produced cedar lumber and promote logging is necessary. A system is also required to ensure that after cutting down the trees, being replanted with less pollen-damaging varieties and remain adequately managed.








